Navigation
Reliable, flexible navigation with high precision
Different areas of application require individual navigation and localization technologies. Through our years of experience, we have the expertise of all market-relevant navigation types in house and offer the coordinated solution for your area of application. From track guided to autonomous we can connect your system with the help of our technologies to increase efficiency and flexibility.
Navigation types

Autonomous navigation
Autonomous navigating vehicles determine the lane independently and act reactively on sensor data. This enables them to avoid obstacles and react flexibly to different situations.
Excerpt of possible areas of application:
- Healthcare, hospitals
- Order picking
- Small parts transport
- Area linking
- Production supply/disposal

Virtual guidance
Virtual guidelines guide the vehicle along a planned path and ensure high efficiency of the transport system. In the process, the vehicle also follows a lane, although this is no longer physically located in the real world. The lanes are planned computer-aided and can be flexibly adjusted at any time.
Excerpt of possible areas of application:
- Strictly structured production environments
- Plant with large throughputs and high efficiency requirements
- Area warehouse
- Production areas with strong change
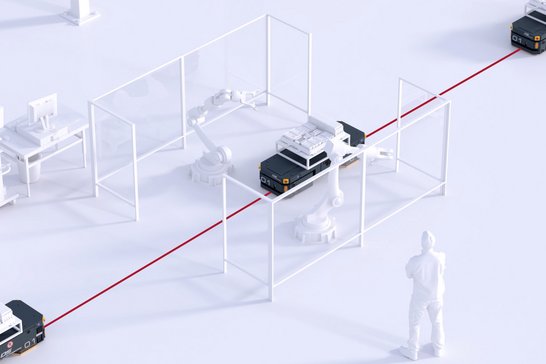
Physical guidance
Physical guidance guide the vehicle along a planned path and ensure high efficiency of the transport system. Suitable sensors are used to detect the physical lane, with magnetic tape guidance lane and active-inductive guidance lane with inductive energy transfer available as technologies. In the event of deviations between the vehicle and the guidance line, the steering motor steers the vehicle back to the desired lane.
Excerpt of possible areas of application:
- Assembly lines
- Simple logistics applications
Choosing the right technology
We know from experience that the choice of the right navigation technology is crucial for reliable function and thus for availability. Thanks to our many years of activity, a wide variety of localization types are available, which can also be combined with each other if required.

Contour-based localization above
With contour-based localization (CBL), mobile robots navigate freely without the need for physical guidelines or infrastructure. This innovative technology, known as contour-based navigation, enables precise vehicle positioning using natural landmarks—eliminating the need for reflectors, magnetic spots, or additional vehicle sensors. At the core of CBL is the laser scanner already integrated into the vehicle for personnel safety. This same scanner is also used for real-time position detection. The system is designed to operate reliably even in dynamic environments, tolerating the presence of people, other vehicles, and moving objects within the scan area. To further enhance positioning accuracy—particularly at transfer stations or handover points—CBL can be easily combined with artificial landmarks if required. This hybrid approach offers maximum flexibility, efficiency, and safety in healthcare and logistics environments.

Advanced Contour-Based Localization with Overhead Laser Scanner
In the overhead contour-based localization (CBL) approach, mobile robots navigate freely—completely infrastructure-free and without physical guide paths. Positioning is achieved using contour-based navigation, a method that relies on natural landmarks instead of reflectors, magnetic spots, or other external aids.
This version of CBL utilizes a high-precision laser scanner mounted on the vehicle's tower. The scanner allows for accurate localization while tolerating the presence of other vehicles, people, or dynamic objects in the scan area. Even in environments with frequently changing conditions, the system ensures reliable positioning at all times.
For areas requiring enhanced precision, such as handover stations, the technology can be seamlessly combined with artificial landmarks, offering maximum flexibility and accuracy in demanding healthcare and logistics environments.

Laser localization
Laser localization uses a laser scanner to detect artificial landmarks in the environment. For this purpose, retroreflective foils are attached to the walls and columns which can be precisely measured by the rotating laser beam even over larger distances. At least 3 marks must be visible at any time so that the position and direction can be determined exactly by means of triangulation.

Magnet localization
Artificial marks (magnetic points) in the ground are used as additional support points for localization. The position of the vehicle is determined by dead reckoning. This requires both precise recording of the odometry data and the bearing of the magnets embedded in the ground at regular intervals.
Here you will find everything you need to know.
The navigation system guides the transport vehicle safely to its destination. To do this, it uses a suitable localization system to determine the vehicle's own position and then follows the path to the destination using path planning.
In lane-guided navigation, the lanes are planned in advance as virtual guidelines. The vehicle follows the manually planned lane exactly and takes the specified traffic rules into account. Precise planning brings out the maximum efficiency and thus solutions for transfer points with high throughput of material can be realized.
Unlike lane-guided systems with physical or virtual guidance, autonomous navigation can independently determine the route to the destination. To do this, the vehicle makes use of the numerous sensors on the vehicles, which record the working environment at all times. Obstacles can be avoided and the flexibility of the system is increased.
Vehicles from DS Automotion are always capable of both autonomous navigation and lane-guided navigation with manually planned guidelines. Autonomous functions are used where flexibility is required. At bottlenecks or transfer points with high throughput, maximum efficiency can be realized by manual planning of lanes and traffic rules.


